Process Description of a slurry Wall made by Stein HT
[according to DIN EN 1538]
Fields of Application
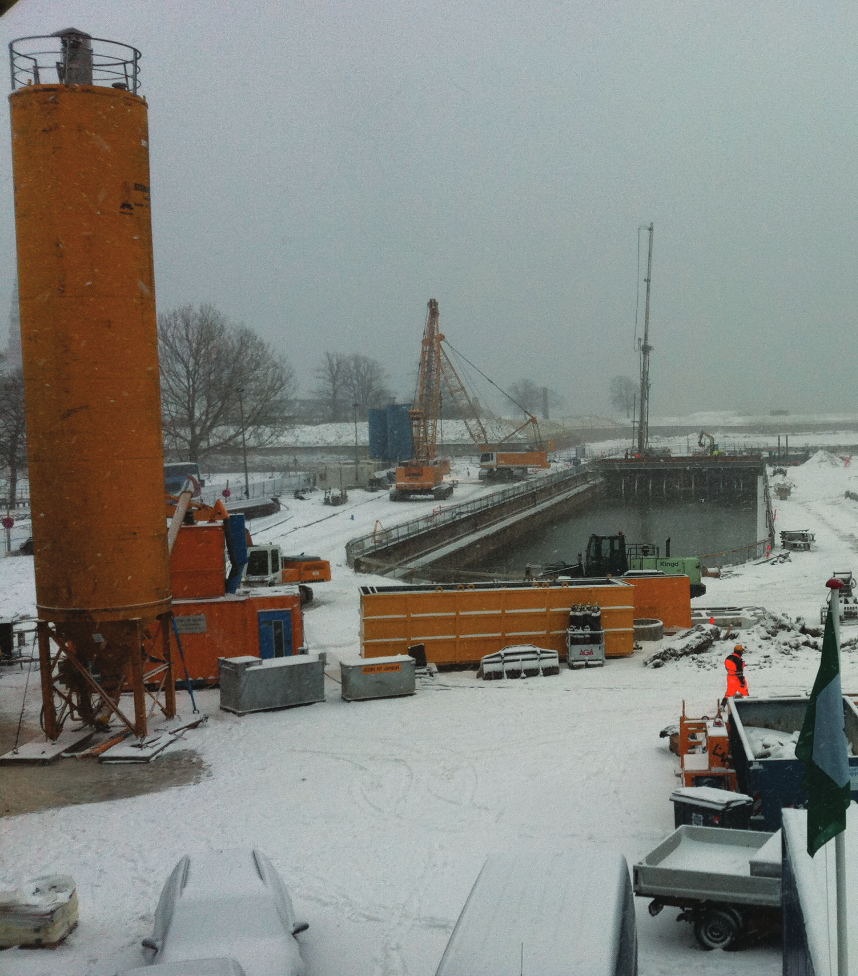
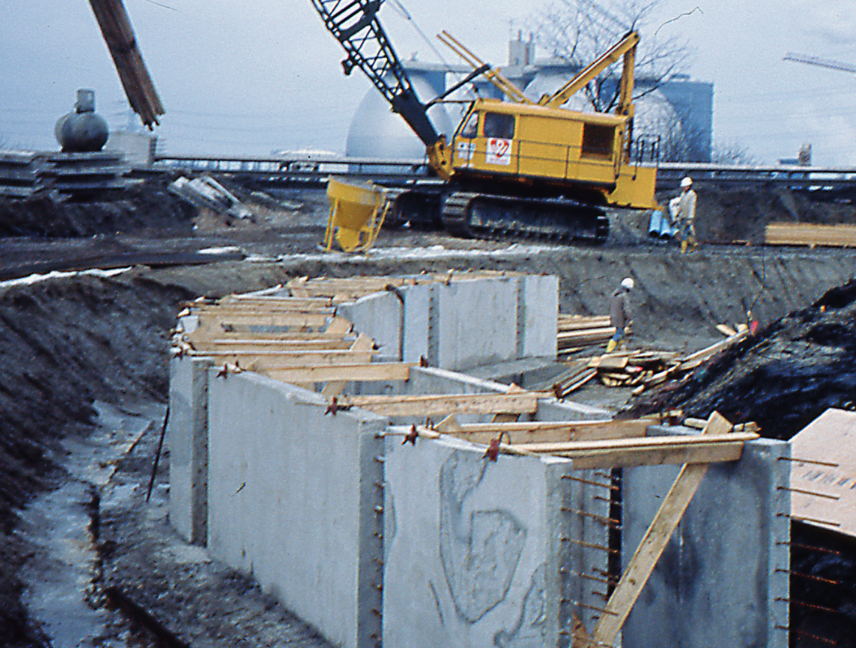
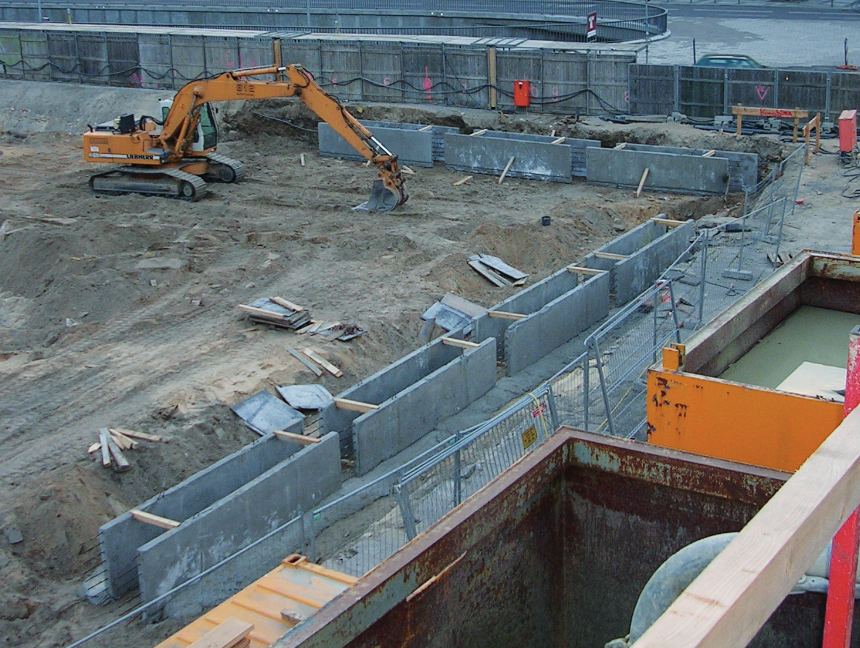
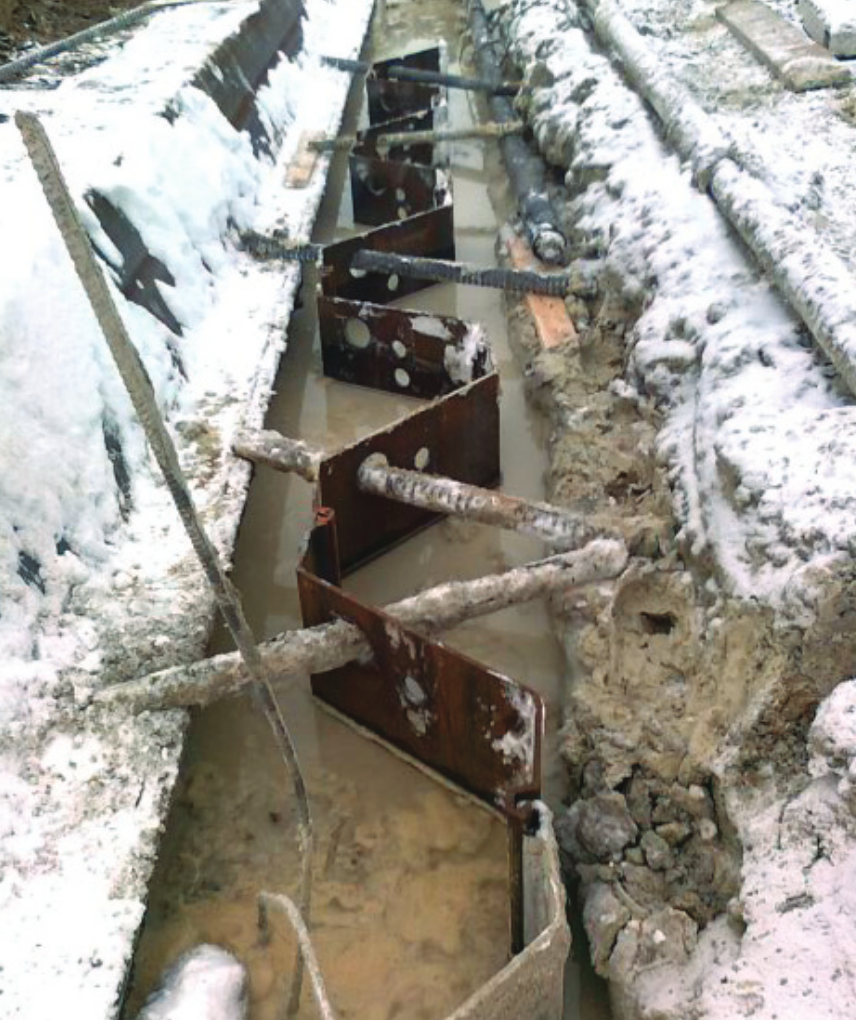
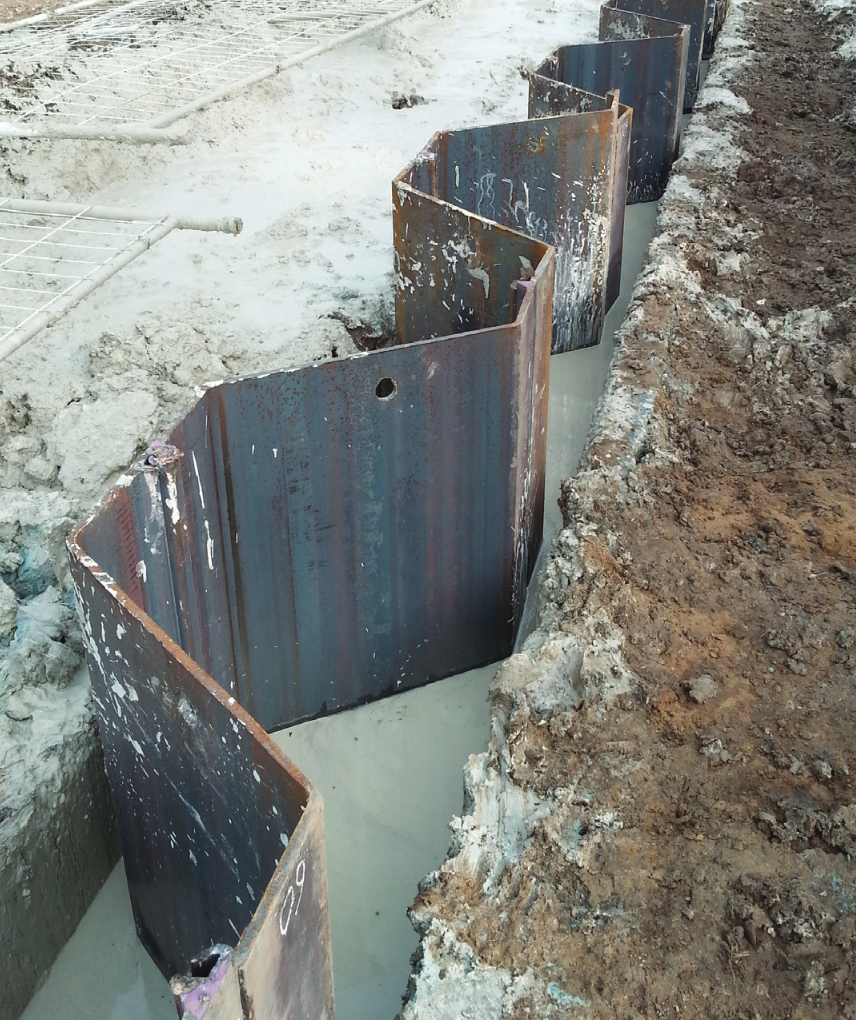
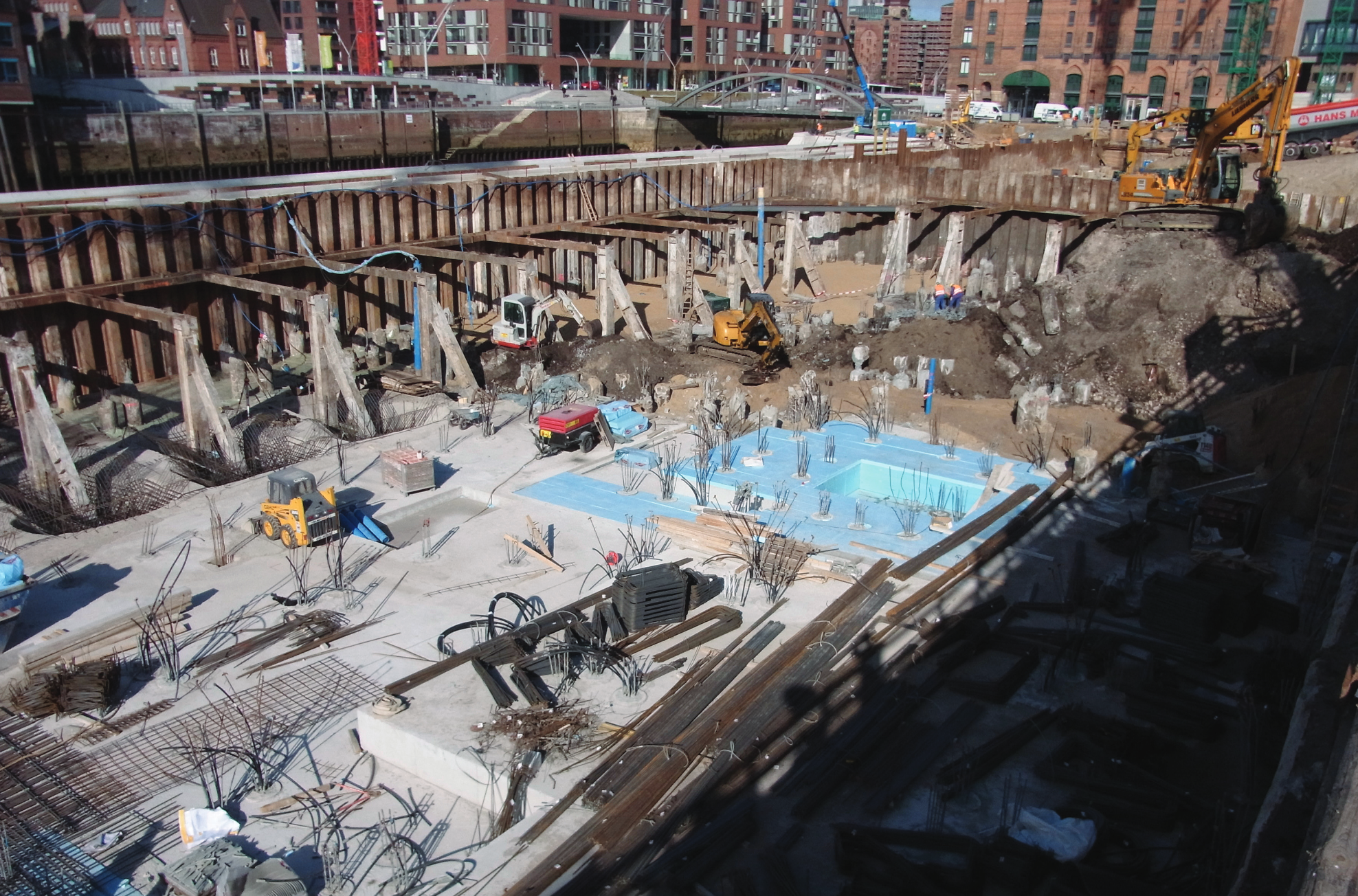
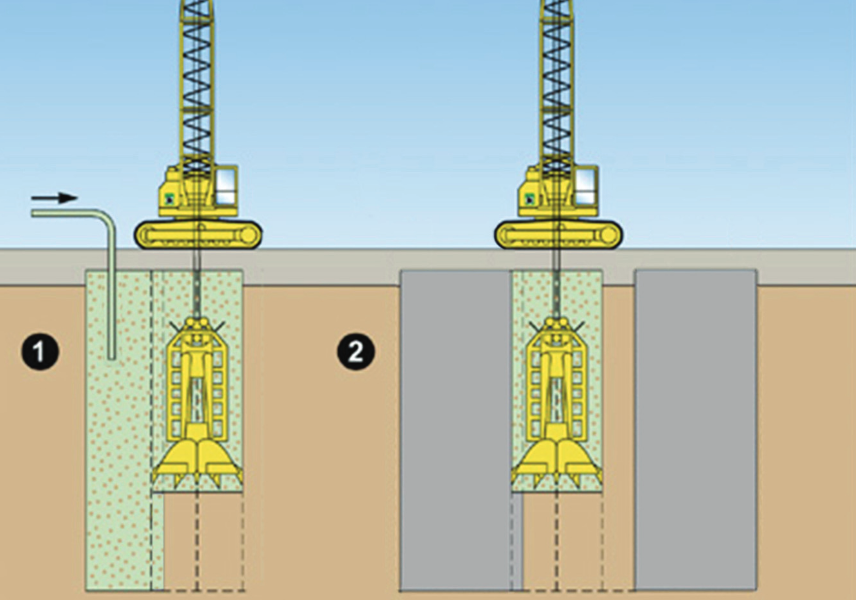
A slurry wall is a vertically executed bentonite-cement wall. It is excavated by means of supporting suspension and has a sealing effect. Both, as a temporary and as a permanent structure, it can also assume structural functions, when combined with sheet piles, girders, or precast units. Wall thicknesses typically range from 600 mm to 1500 mm and depths of max. 40 m are usual, although thicknesses of max. 2000 mm and considerably deeper walls are feasible.
A slurry wall is usually (but not exclusively) used for the following structures:
- Enclosure/stabilisation of building pits
- Pipe jacking shafts/entrance blocks
- Sealing blocks
- Sluices (as sheet-pile wall)
- Landfill enclosures
- Transverse bulkhead for partitioning of building pits
The advantages of a slurry wall in comparison to other foundation processes are as follows:
- Low-noise and low-vibration construction
- Low deformation
- Shorter construction period as against e.g., bored pile walls
- Sealing effect