Process Description of a Diaphragm Wall made by Stein HT
[according to DIN EN 1538]
Preface/Fields of Application
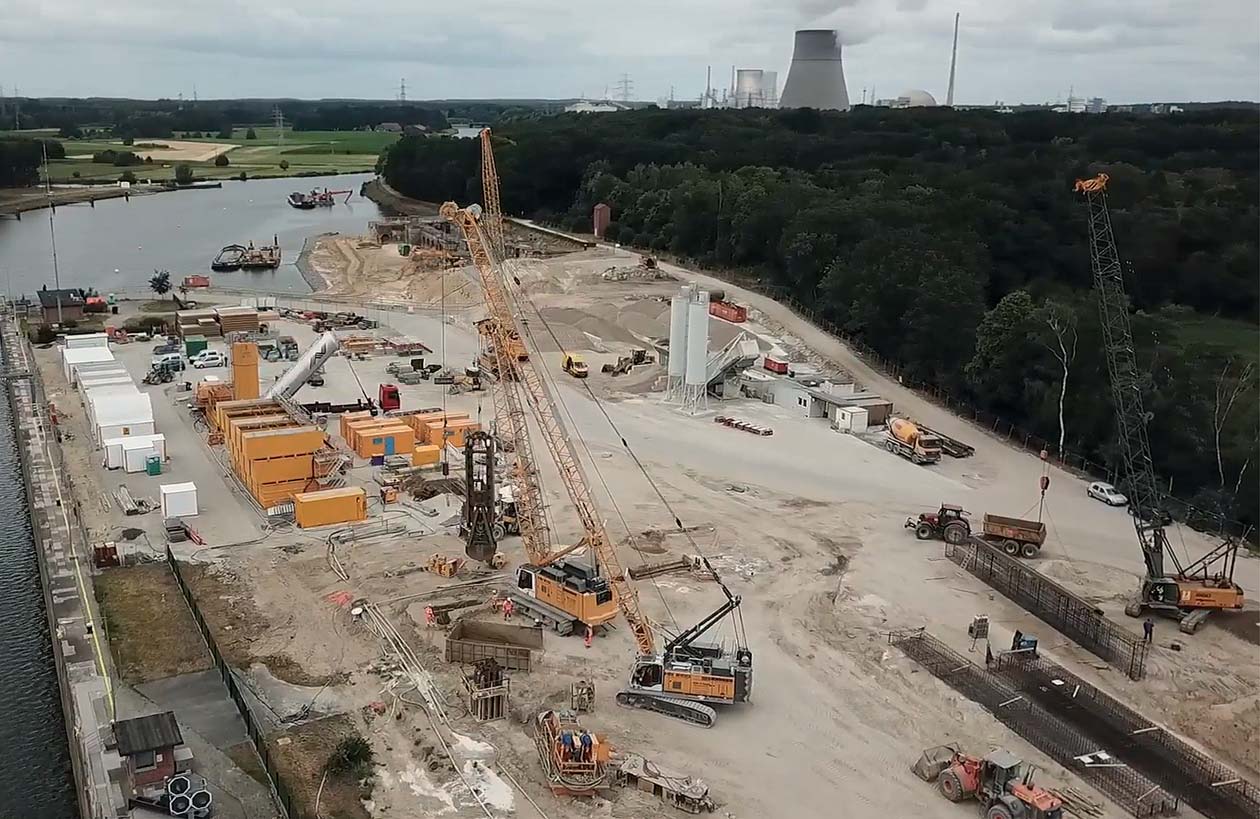
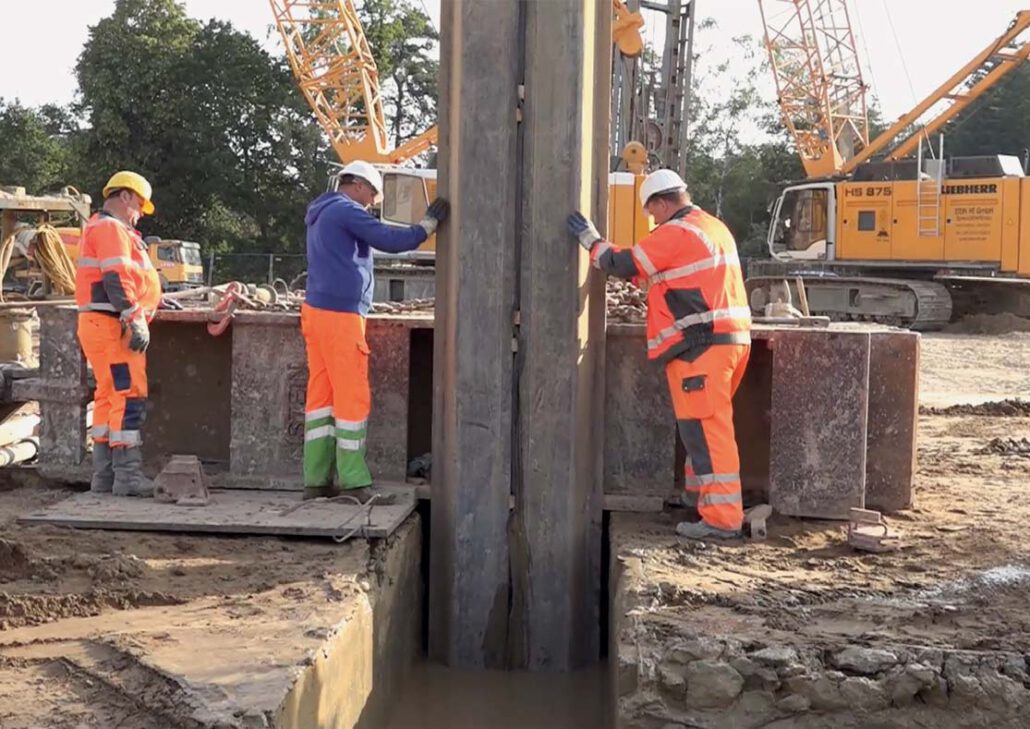
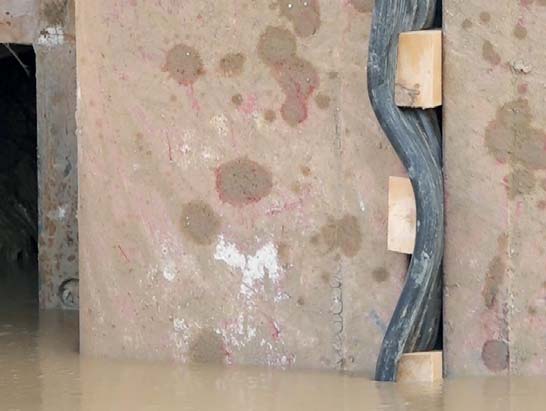
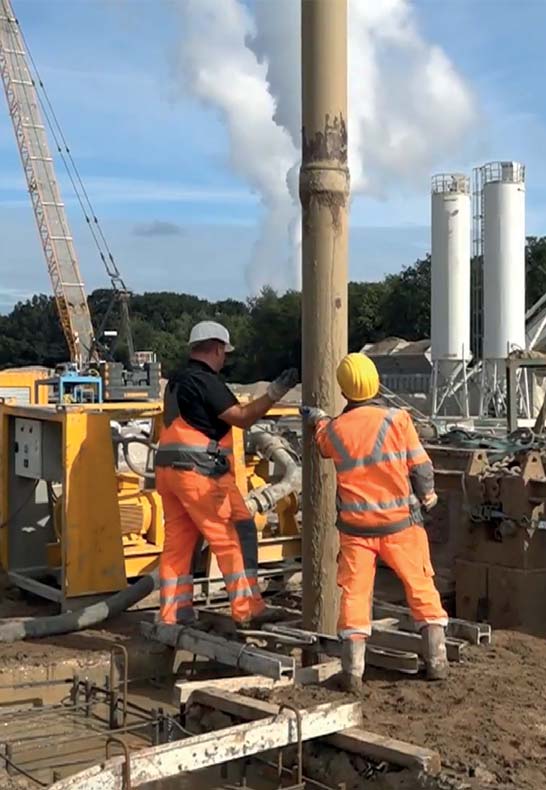
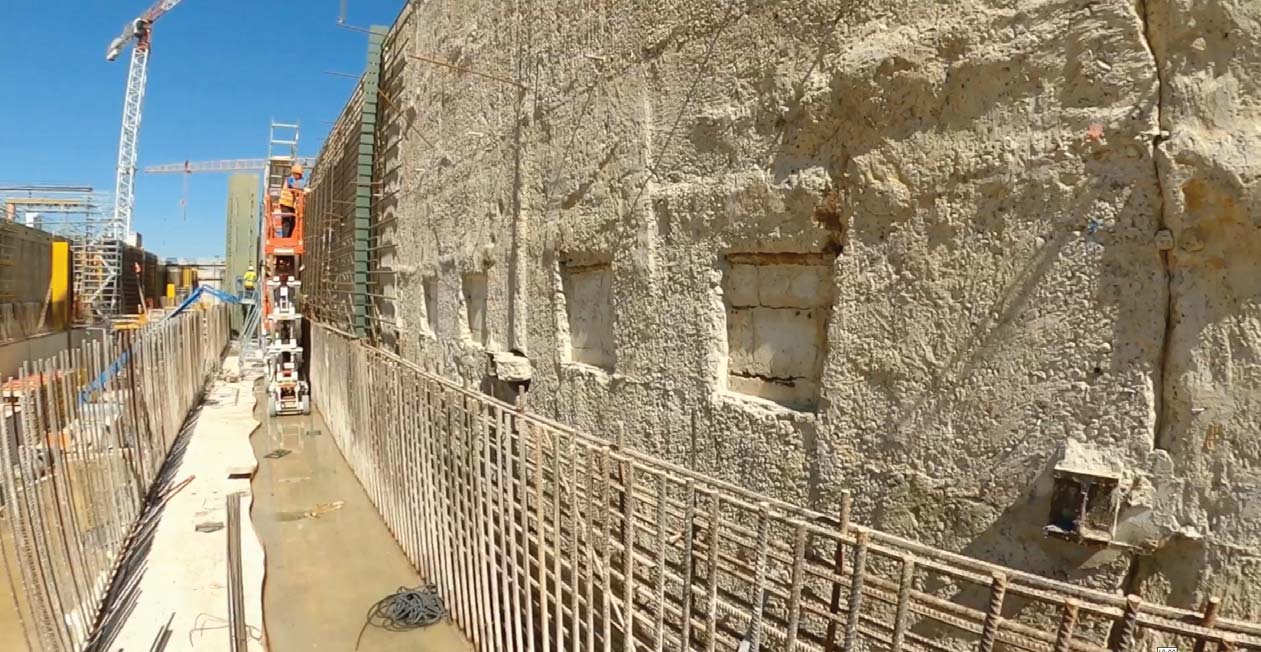
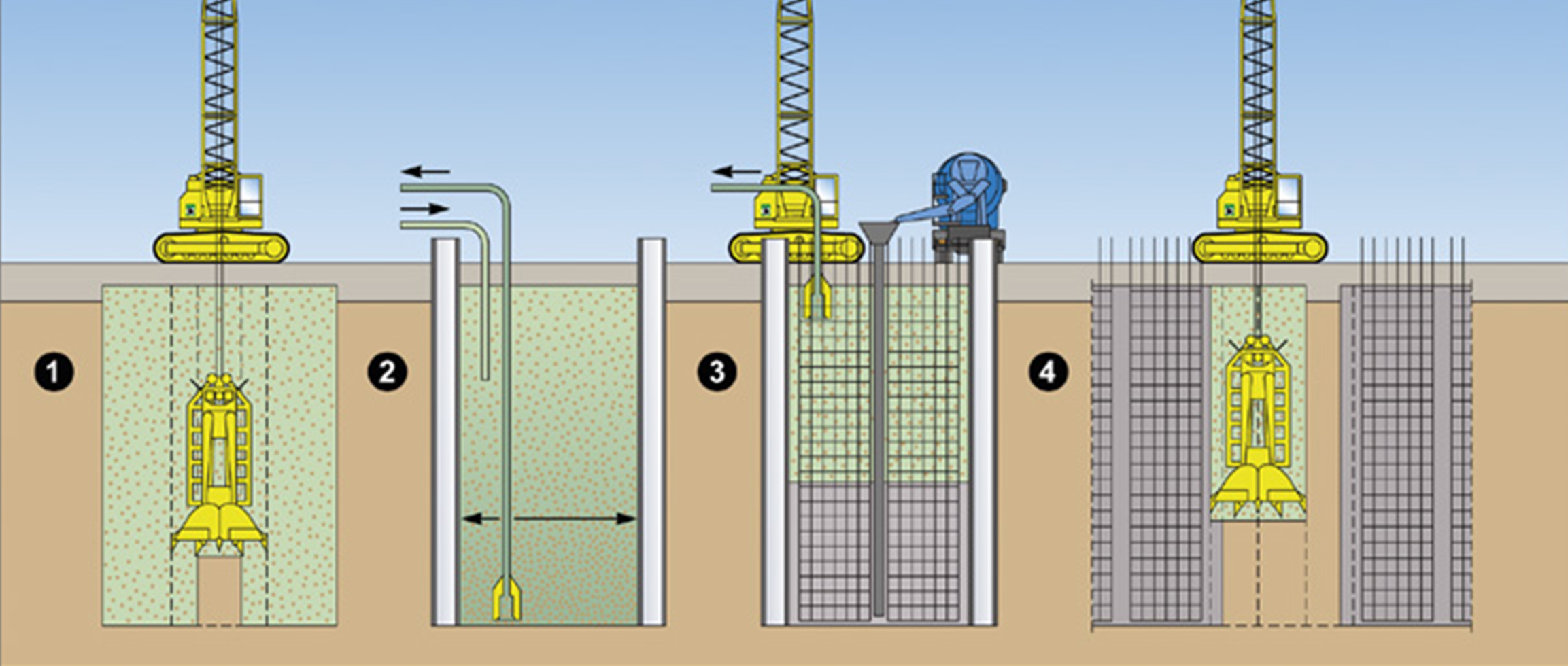
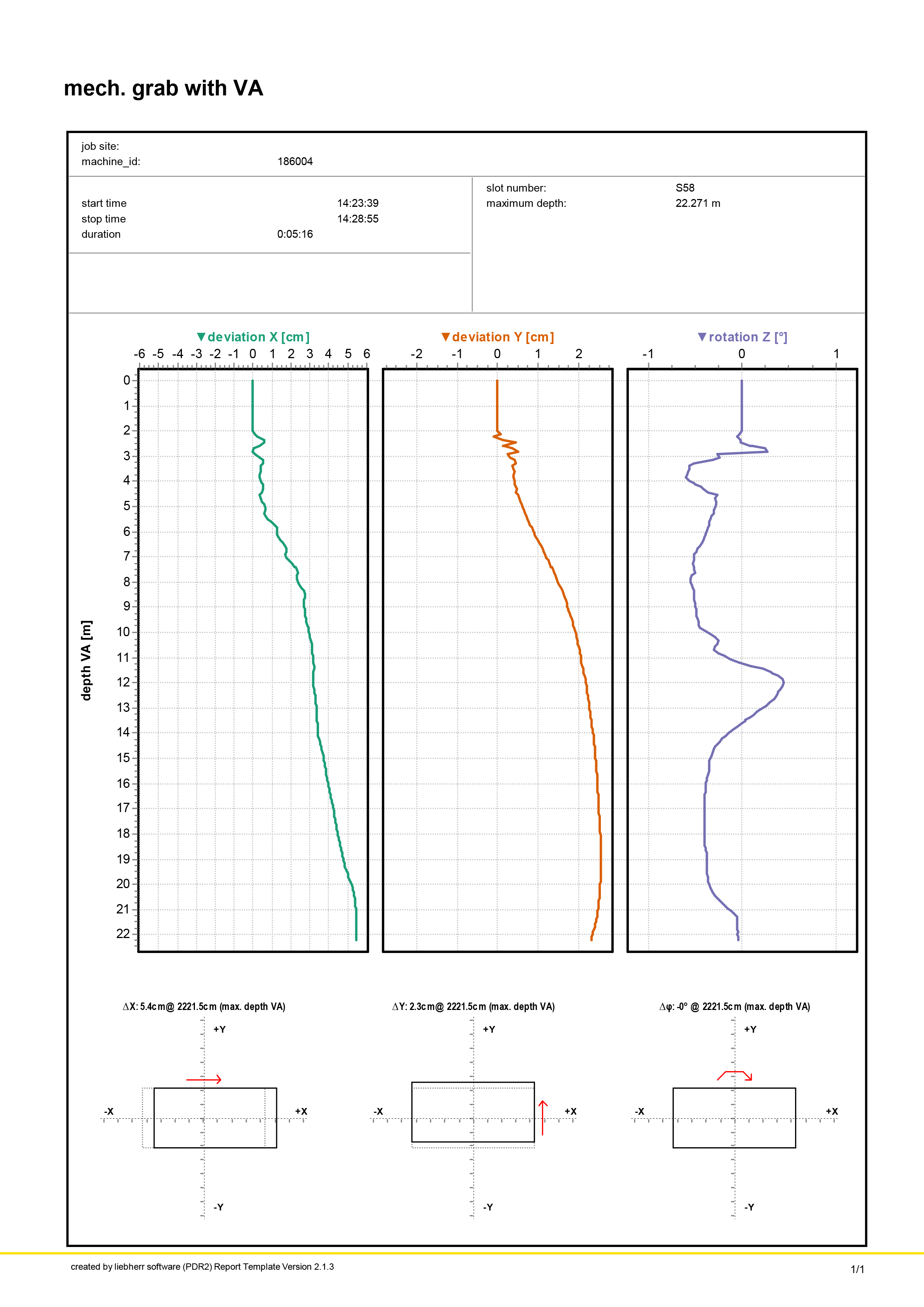
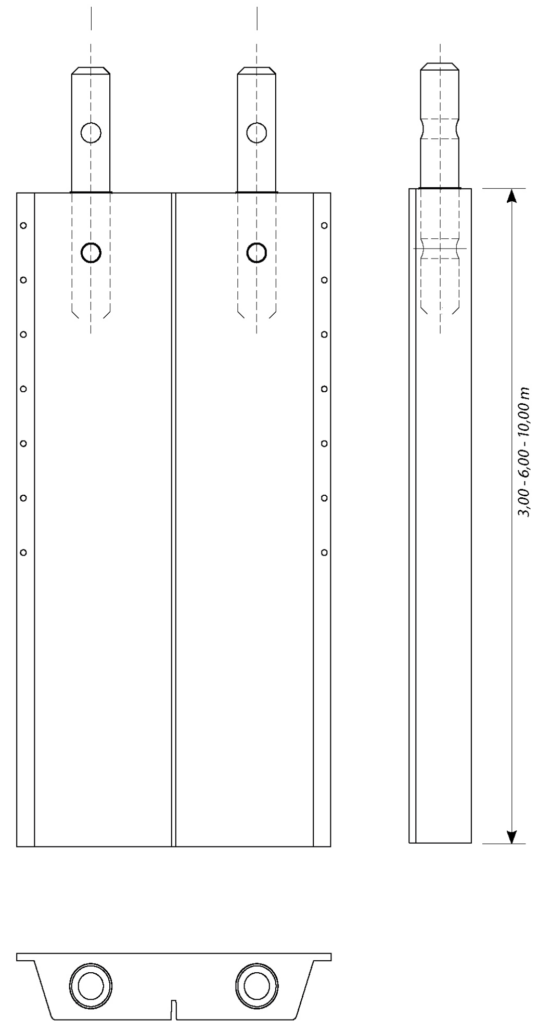
A diaphragm wall is a vertically executed reinforced concrete wall. It is excavated by means of supporting suspension and has a sealing effect. Both, as a temporary and as a permanent structure, it can also assume load-bearing/load-transferring functions. Wall thicknesses typically range from 600 mm to 1500 mm and depths of max. 40 m are usual, although thicknesses of max. 2000 mm and considerably deeper walls are feasible.
A diaphragm wall is usually (but not exclusively) used for the following structures:
- Tunnel and underground construction
- Enclosure/stabilisation of building pits
- Pipe jacking shafts
- Underground car parks
- Inner-city building pits
- sluices
- Landfill enclosures
- As foundation element (barrettes)
The advantages of a diaphragm wall in comparison to other foundation processes are as follows:
- Low-noise and low-vibration construction
- Low deformation
- In case of adequate statics, it can bear very high loads
- Shorter construction period in comparison to e.g. bored pile walls
- Sealing effect